Step: 6
In this section, we are going to discuss the required script files for Magento installation using a remote provisioner.
The below is the file which is used to create a database username, password and privileges on a remote server at the time of execution.
sudo nano dbdetails.sh
#Database script file
#!/bin/bash
# Functions
ok() { echo -e '\e[32m'$1'\e[m'; } # Green
EXPECTED_ARGS=3
E_BADARGS=65
MYSQL=`which mysql`
Q1="CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS $1;"
Q2="GRANT ALL ON *.* TO '$2'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY '$3';"
Q3="FLUSH PRIVILEGES;"
SQL="${Q1}${Q2}${Q3}"
if [ $# -ne $EXPECTED_ARGS ]
then
echo "Usage: $0 dbname dbuser dbpass"
exit $E_BADARGS
fi
$MYSQL -e "$SQL"
ok "Database $1 and user $2 created with a password $3"
This is the script used to set up a server block in Nginx with the domain name.
sudo nano serverblock.sh
#Nginx server block with the domain name
#!/usr/bin/env bash
#
# Nginx - new server block
# Based on this post: http://clubmate.fi/how-to-make-an-nginx-server-block-manually-or-with-a-shell-script/
# Functions
ok() { echo -e '\e[32m'$1'\e[m'; } # Green
die() { echo -e '\e[1;31m'$1'\e[m'; exit 1;
# Variables
NGINX_AVAILABLE_VHOSTS='/etc/nginx/sites-available'
NGINX_ENABLED_VHOSTS='/etc/nginx/sites-enabled'
WEB_DIR='/var/www'
WEB_USER='www-data'
USER='root'
NGINX_SCHEME='$scheme'
NGINX_REQUEST_URI='$request_uri'
URI='$uri'
ARGS='$args'
DOCUMENT_ROOT='$document_root'
FASTCGI_SCRIPT_NAME='$fastcgi_script_name'
# Sanity check
[ $(id -g) != "0" ] && die "Script must be run as root."
[ $# != "1" ] && die "Usage: $(basename $0) domainName"
# Create Nginx config file
cat > $NGINX_AVAILABLE_VHOSTS/$1 <<EOF
upstream fastcgi_backend {
server unix:/run/php/php7.2-fpm.sock;
}
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
set $MAGE_ROOT /var/www/$1/public_html;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
server_name $1 www.$1;
include /var/www/$1/public_html/nginx.conf.sample;
location ~ \.php$ {
try_files $URI =404;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(/.+)$;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.2-fpm.sock;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $DOCUMENT_ROOT$FASTCGI_SCRIPT_NAME;
include fastcgi_params;
}
# Logs
access_log $WEB_DIR/$1/logs/access.log;
error_log $WEB_DIR/$1/logs/error.log;
}
EOF
# Creating {public, log} directories
mkdir -p $WEB_DIR/$1/{public_html,logs}
touch $WEB_DIR/$1/logs/access.log
touch $WEB_DIR/$1/logs/error.log
# Creating index.html file
cat > $WEB_DIR/$1/public_html/index.html <<EOF
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>$1</title>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
</head>
<body class="container">
<header><h1>$1<h1></header>
<div id="wrapper">
Hello World
</div>
<footer>© $(date +%Y)</footer>
</body>
</html>
EOF
# Changing permissions
chown -R $USER:$WEB_USER $WEB_DIR/$1
# Enable site by creating symbolic link
ln -s $NGINX_AVAILABLE_VHOSTS/$1 $NGINX_ENABLED_VHOSTS/$1
# Restart
#echo "Do you wish to restart nginx?"
#select yn in "Yes" "No"; do
# case $yn in
# Yes ) /etc/init.d/nginx restart ; break;;
# No ) exit;;
# esac
#done
ok "Site Created for $1"
This is the file used to install Magento on a remote server.
sudo nano magento_install.sh
#Magento installation script echo "Lets install magento" cd /var/www/$12/public_html sudo chmod -R 777 var pub app generated #php bin/magento setup:install \ #--base-url=$1 \ #--db-host="$2 \ #--db-name=$3 \ #--db-user=$4 \ #--db-password=$5 \ #--admin-firstname=$6 \ #--admin-lastname=$7 \ #--admin-email=$6 \ #--admin-user=$7 \ #--admin-password=$8 \ #--backend-frontname=$9 \ php bin/magento setup:install --base-url=$1 \ --db-host=$2 --db-name=$3 --db-user=$4 --db-password=$5 --admin-firstname=$6 --admin-lastname=$7 \ --admin-email=$8 --admin-user=$9 --admin-password=$10 --backend-frontname=$11 \ --language=en_US --currency=USD --timezone=America/Chicago --use-rewrites=1 #After installing Magento we need to give permission cd /var/www/$12/public_html sudo chmod -R 777 var pub app generated echo "check your website now!!"
Note: The $ symbol here, refers to use the same values which we get from users. It is these user inputs that are passed across the script files using $ notations.
Step: 7
Now that we have declared variables, the Nginx server block script installed required Magento packages and script permissions, let’s start proceeding with the main configuration file.
sudo nano sample.tf
#Droplet section
resource "digitalocean_droplet" "testing" {
image = "ubuntu-18-04-x64"
name = "testing"
region = "nyc1"
size = "2GB"
private_networking = true
ssh_keys = [
"${var.ssh_fingerprint}"
]
#Connection section
connection {
user = "root"
type = "ssh"
private_key = "${file(var.pvt_key)}"
timeout = "3m"
host = "${digitalocean_droplet.testing.ipv4_address}"
}
#Nginx server block script
provisioner "file" {
source = "serverblock.sh"
destination = "/tmp/serverblock.sh"
}
#Database details
provisioner "file" {
source = "db_details.sh"
destination = "/tmp/db_details.sh"
}
#Magento file
provisioner "file" {
source = "magento.tar.gz"
destination = "/tmp/magento.tar.gz"
}
#Additional script
provisioner "file" {
source = "additional.sh"
destination = "/tmp/additional.sh"
}
#Magento installation script
provisioner "file" {
source = "magento_install.sh"
destination = "/tmp/magento_install.sh"
}
#Installation of the required things
provisioner "remote-exec" {
inline = [
"export PATH=$PATH:/usr/bin",
# install nginx
"sudo apt-get update",
"sudo apt-get -y install nginx && sudo apt-get -y install varnish && sudo apt-get install -y mysql-server && sudo apt-get install -y php7.2-fpm && chmod +x /tmp/serverblock.sh && /tmp/serverblock.sh ${var.domain_Name} && chmod +x /tmp/db_details.sh && /tmp/db_details.sh ${var.dbname} ${var.dbuser} ${var.dbpass} && chmod +x /tmp/additional.sh && /tmp/additional.sh ${var.domain_Name} && chmod +x /tmp/magento_install.sh && /tmp/magento_install.sh ${var.baseurl} ${var.dbhost} ${var.dbname} ${var.dbuser} ${var.dbpass} ${var.admin_firstname} ${var.admin_lastname} ${var.admin_email} ${var.admin_user} ${var.admin_password} ${var.backend_frontname} ${var.domain_Name}"
]
}
}
Make sure you have the Magento file and don’t forget to add a path in the source section.
Note:
- Download the Magento packages on your local system.
- Next, upload the downloaded packages to your remote server as you upload the script files.
- In which, Source denotes the path in which you downloaded the packages.
- And, Destination is where you desired to upload the packages.
- Here, you need to assign permissions for the script file as generally, the script file will not execute until and unless permissions are assigned.
Step: 8
After the successful configuration, we shall proceed with the output execution phase.
The output of terraform init
Initialize the terraform
terraform init
You shall see an output like below:
Output Initializing the backend... Initializing provider plugins... The following providers do not have any version constraints in configuration, so the latest version was installed. To prevent automatic upgrades to new major versions that may contain breaking changes, it is recommended to add version = "..." constraints to the corresponding provider blocks in configuration, with the constraint strings suggested below. * provider.digitalocean: version = "~> 1.12" Terraform has been successfully initialized! You may now begin working with Terraform. Try running "terraform plan" to see any changes that are required for your infrastructure. All Terraform commands should now work. If you ever set or change modules or backend configuration for Terraform, rerun this command to reinitialize your working directory. If you forget, other commands will detect it and remind you to do so if necessary.
The output of terraform validate
Terraform validate
Output Success! The configuration is valid.
The output of terraform plan
terraform plan
var.admin_email
Enter a value: abc@123.com
var.admin_firstname
Enter a value: first
var.admin_lastname
Enter a value: last
var.admin_password
Enter a value: Abc@123
var.admin_user
Enter a value: firstlast
var.backend_frontname
Enter a value: admin
var.baseurl
Enter a value: http://sample.com
var.dbhost
Enter a value: localhost
var.dbname
Enter a value: magento
var.dbpass
Enter a value: magento123
var.dbuser
Enter a value: magento
var.domain_Name
Enter a value: sample.com
var.droplet_location
Enter a value: nyc1
var.droplet_size
Enter a value: 2gb
Refreshing Terraform state in-memory prior to plan...
The refreshed state will be used to calculate this plan, but will not be
persisted to local or remote state storage.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
An execution plan has been generated and is shown below.
Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols:
+ create
Terraform will perform the following actions:
# digitalocean_droplet.testing will be created
+ resource "digitalocean_droplet" "testing" {
+ backups = false
+ created_at = (known after apply)
+ disk = (known after apply)
+ id = (known after apply)
+ image = "ubuntu-18-04-x64"
+ ipv4_address = (known after apply)
+ ipv4_address_private = (known after apply)
+ ipv6 = false
+ ipv6_address = (known after apply)
+ ipv6_address_private = (known after apply)
+ locked = (known after apply)
+ memory = (known after apply)
+ monitoring = false
+ name = "testing"
+ price_hourly = (known after apply)
+ price_monthly = (known after apply)
+ private_networking = true
+ region = "nyc1"
+ resize_disk = true
+ size = "c-2"
+ ssh_keys = [
+ "89:ff:cb:c1:20:97:f8:fe:68:77:72:ce:fe:2a:cf:b7",
]
+ status = (known after apply)
+ urn = (known after apply)
+ vcpus = (known after apply)
+ volume_ids = (known after apply)
}
Plan: 1 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Note: You didn't specify an "-out" parameter to save this plan, so Terraform
can't guarantee that exactly these actions will be performed if
"terraform apply" is subsequently run.
You need to twice enter the user inputs; one during the terraform plan command and the other during the terraform apply command. To skip this repetition, you can directly give the user inputs during the latter phase.
The output of terraform apply
terraform apply
Since, we have installed several technologies, displaying the execution of full output in a single stretch is likely to be irksome. That’s why the output here is divided into Output 1 and Output 2.
Output 1
Enter the following details correctly
var.admin_email
Enter a value: abc@123.com
var.admin_firstname
Enter a value: first
var.admin_lastname
Enter a value: last
var.admin_password
Enter a value: Abc@123
var.admin_user
Enter a value: firstlast
var.backend_frontname
Enter a value: admin
var.baseurl
Enter a value: http://sample.com
var.dbhost
Enter a value: localhost
var.dbname
Enter a value: magento
var.dbpass
Enter a value: magento123
var.dbuser
Enter a value: magento
var.domain_Name
Enter a value: sample.com
var.droplet_location
Enter a value: nyc1
var.droplet_size
Enter a value: 2gb
An execution plan has been generated and is shown below.
Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols:
+ create
Terraform will perform the following actions:
# digitalocean_droplet.testing will be created
+ resource "digitalocean_droplet" "testing" {
+ backups = false
+ created_at = (known after apply)
+ disk = (known after apply)
+ id = (known after apply)
+ image = "ubuntu-18-04-x64"
+ ipv4_address = (known after apply)
+ ipv4_address_private = (known after apply)
+ ipv6 = false
+ ipv6_address = (known after apply)
+ ipv6_address_private = (known after apply)
+ locked = (known after apply)
+ memory = (known after apply)
+ monitoring = false
+ name = "testing"
+ price_hourly = (known after apply)
+ price_monthly = (known after apply)
+ private_networking = true
+ region = "nyc1"
+ resize_disk = true
+ size = "c-2"
+ ssh_keys = [
+ "89:ff:cb:c1:20:97:f8:fe:68:77:72:ce:fe:2a:cf:b7",
]
+ status = (known after apply)
+ urn = (known after apply)
+ vcpus = (known after apply)
+ volume_ids = (known after apply)
}
Plan: 1 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
Do you want to perform these actions?
Terraform will perform the actions described above.
Only 'yes' will be accepted to approve.
Enter a value: yes
digitalocean_droplet.testing: Creating...
digitalocean_droplet.testing: Still creating... [10s elapsed]
digitalocean_droplet.testing: Still creating... [20s elapsed]
digitalocean_droplet.testing: Provisioning with 'file'...
digitalocean_droplet.testing: Still creating... [30s elapsed]
digitalocean_droplet.testing: Still creating... [40s elapsed]
digitalocean_droplet.testing: Provisioning with 'file'...
digitalocean_droplet.testing: Provisioning with 'file'...
digitalocean_droplet.testing: Still creating... [50s elapsed]
digitalocean_droplet.testing: Still creating... [1m0s elapsed]
digitalocean_droplet.testing: Still creating... [1m10s elapsed]
digitalocean_droplet.testing: Still creating... [1m20s elapsed]
digitalocean_droplet.testing: Still creating... [1m30s elapsed]
digitalocean_droplet.testing: Still creating... [1m40s elapsed]
digitalocean_droplet.testing: Provisioning with 'file'...
digitalocean_droplet.testing: Provisioning with 'file'...
digitalocean_droplet.testing: Still creating... [1m50s elapsed]
digitalocean_droplet.testing: Provisioning with 'file'...
digitalocean_droplet.testing: Provisioning with 'file'...
digitalocean_droplet.testing: Still creating... [2m0s elapsed]
digitalocean_droplet.testing: Provisioning with 'file'...
digitalocean_droplet.testing: Provisioning with 'remote-exec'...
digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): Connecting to remote host via SSH...
digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): Host: 67.205.164.118
digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): User: root
digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): Password: false
digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): Private key: true
digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): Certificate: false
digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): SSH Agent: true
digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): Checking Host Key: false
digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): Connected!
Output 2
digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): Module 'Magento_WishlistSampleData': digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): [Progress: 924 / 941] digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): Module 'Amazon_Core': digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): [Progress: 925 / 941] digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): Module 'Amazon_Login': digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): [Progress: 926 / 941] digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): Module 'Amazon_Payment': digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): [Progress: 927 / 941] digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): Module 'Dotdigitalgroup_Email': digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): [Progress: 928 / 941] digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): Module 'Klarna_Core': digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): [Progress: 929 / 941] digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): Module 'Klarna_Ordermanagement': digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): [Progress: 930 / 941] digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): Module 'Klarna_Kp': digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): [Progress: 931 / 941] digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): Module 'Magento_PaypalReCaptcha': digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): [Progress: 932 / 941] digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): Module 'MSP_TwoFactorAuth': digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): [Progress: 933 / 941] digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): Module 'Temando_Shipping': digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): [Progress: 934 / 941] digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): Module 'Vertex_Tax': digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): [Progress: 935 / 941] digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): [Progress: 936 / 941] digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): Installing admin user... digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): [Progress: 937 / 941] digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): Caches clearing: digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): Cache cleared successfully digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): [Progress: 938 / 941] digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): Disabling Maintenance Mode: digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): [Progress: 939 / 941] digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): Post installation file permissions check... digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): For security, remove write permissions from these directories: '/var/www/sample.com/public_html/app/etc' digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): [Progress: 940 / 941] digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): Write installation date... digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): [Progress: 941 / 941] digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): [SUCCESS]: Magento installation complete. digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): [SUCCESS]: Magento Admin URI: /admin digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): Nothing to import. digitalocean_droplet.testing (remote-exec): check your website now!! digitalocean_droplet.testing: Creation complete after 7m31s [id=174043601] Apply complete! Resources: 1 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
Step: 9
After successful execution of the above script, it takes 7 to 10 minutes to get completed. Once it is done, you need to add the domain name or server name into your etc/hosts as we did not configure a real-time DNS name.
Open the file called
sudo nano /etc/hosts 67.205.164.118 sample.com www.sample.com
Now, you will be able to see the Magento installation in your browser, http://sample.com
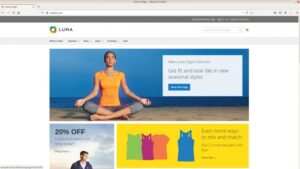
Note: Here, we have installed Varnish for general purpose, if you want to configure Varnish with Magento, visit the link, https://adoltech.com/blog/enhancing-magentos-performance-with-varnish-cache/
In this article, a basic introduction about Magento, Terraform, Remote Exec. Provisioner and other prerequisites have been disclosed. Further, we have installed Magento, it’s required packages along with some of the technologies such as Nginx, MySQL and Varnish. Also, it is to be remembered that we have installed Varnish only for general purpose, to carry out advanced settings, kindly visit the above-mentioned link. As said before, you can also install some of your other desired technologies in the same configuration file. Thus, this is all about the effective and quick way in which you install Magento with other technologies using Terraform.